NLP Course - Statistical Language Models Notebook
Introduction to Language Models
Language models (LMs) are statistical tools that estimate the probability of a sequence of words or predict the next word in a sequence. They are foundational to natural language processing tasks like text generation, speech recognition, and machine translation.
Key Concepts
- Probability Distribution: A language model assigns a probability to a sequence of words, denoted as P(w₁, w₂, ..., wₙ).
- Prediction Task: Given a context of previous words, predict the next word, i.e., P(wₙ | w₁, ..., wₙ₋₁).
- Applications: Autocomplete, spelling correction, and text generation.
Statistical Language Models
Statistical language models rely on frequency counts from a text corpus to estimate word sequence probabilities. They are based on observed patterns in data and are commonly used in n-gram models.
Key Features
- Data-Driven: Probabilities are derived from the frequency of word sequences in a corpus.
- Scalability: Suitable for small to medium-sized corpora but can face issues with larger contexts.
- Applications: Speech recognition, predictive text input, and machine translation.
Bayes Decomposition
Bayes decomposition, or the chain rule of probability, breaks down the joint probability of a word sequence into a product of conditional probabilities.
Mathematical Formulation
This expresses the probability of a sequence as the product of the probability of each word given all previous words.
Key Points
- Context: Full context (all previous words) is computationally expensive to model.
- Simplification: Practical models limit the context using assumptions like the Markov assumption.
- Applications: Used in statistical models to estimate sequence probabilities.
Maximum Likelihood Estimation
Maximum Likelihood Estimation (MLE) estimates the parameters of a language model by maximizing the likelihood of the observed data, typically using frequency counts.
Mathematical Formulation
For an n-gram model, the MLE for the conditional probability is:
Where count represents the frequency of the sequence in the corpus.
Key Points
- Estimation: MLE calculates probabilities based on observed frequencies.
- Zero Probability Issue: Unseen n-grams get zero probability, necessitating smoothing techniques.
- Example: For a bigram "the cat," P(cat | the) = count(the cat) / count(the).
Markov Assumption
The Markov assumption simplifies language modeling by assuming that the probability of a word depends only on a fixed number of previous words, rather than the entire sequence.
Mathematical Formulation
For an n-gram model with a Markov assumption of order k (where k = n-1):
For example, in a bigram model (k=1), the probability of a word depends only on the immediately preceding word.
Key Points
- Order: A first-order Markov model corresponds to bigrams, second-order to trigrams, etc.
- Trade-off: Higher-order models capture more context but increase data sparsity.
- Applications: Simplifies computation in predictive text and speech recognition.
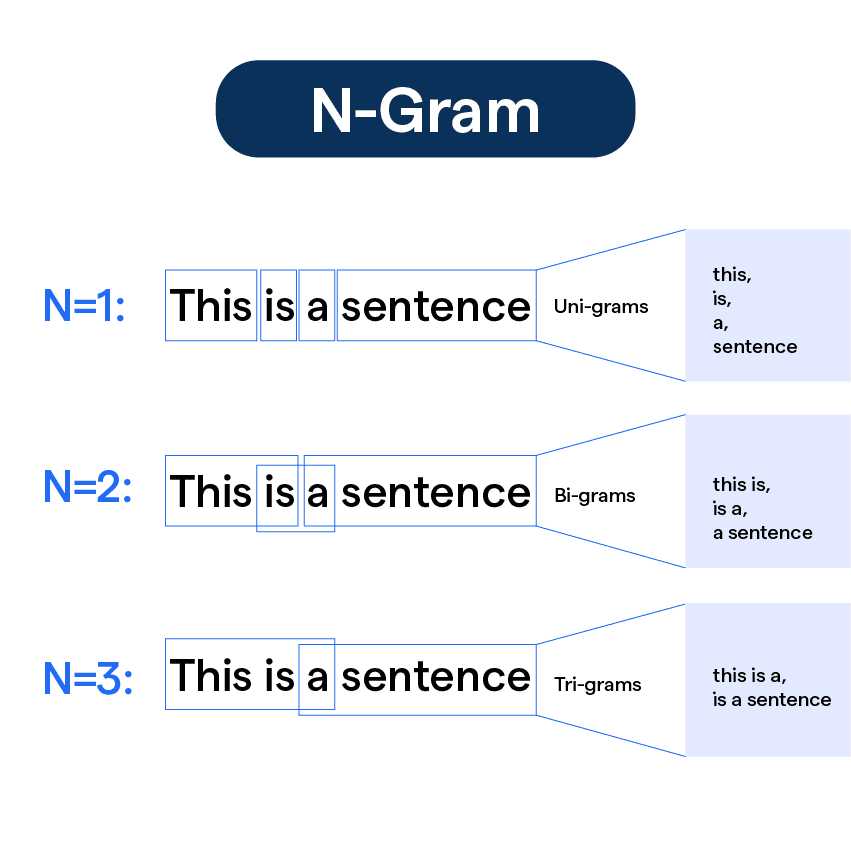
N-Gram Models
N-gram models are a type of statistical language model that predict the next word based on the previous n-1 words, using frequency counts from a corpus. An n-gram is a contiguous sequence of n words.
Types of N-Grams
- Unigram (n=1): Models individual words independently, e.g., P(w₁).
- Bigram (n=2): Models pairs of consecutive words, e.g., P(w₂ | w₁).
- Trigram (n=3): Models triplets of consecutive words, e.g., P(w₃ | w₁, w₂).
- Higher-Order N-Grams: Use larger contexts (n>3), but face data sparsity issues.
Key Points
- Strengths: Simple to implement, computationally efficient, and effective for short-term dependencies.
- Limitations: Struggle with long-range dependencies and unseen n-grams (data sparsity).
- Smoothing: Techniques like Laplace or Kneser-Ney are used to handle zero probabilities for unseen n-grams.
Example: Bigram Probability
Calculating the probability of "the cat" in a corpus.